| Comparison: C, C++, Java | |
|---|---|
|
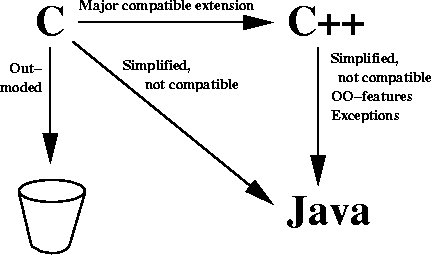
|
Comparison: C, C++, Java |
| Comparison: C, C++, Java | |
|---|---|
|

|
| Feature | C | C++ | Java |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comments | /* This is a C-style comment */ |
/* C-style comment */ // C++ and Java |
/* C-style comment */ // C++ and Java |
| Null pointer | NULL (preferred) (needs #include <stdio.h>) 0 (allowed) |
0 (preferred) NULL (with #include <stdio.h>) |
null |
| Constants | #define PI 3.141592653590 | const double PI = 3.14159265358979; (also allowed in C) |
final double PI = 3.14159265358979; or Math.PI |
| Declarations | At beginning of a block (can be used thereafter) |
Anywhere in a block (can be used thereafter) |
Anywhere in a block (can be used thereafter) |
| Macros | #define ABS(x) ((x)>0 ? (x) : -(x)) |
inline abs(int x) {
return(x>0 ? x : -x);} |
No macros |
| Arrays | int x[10]; |
int x[10]; |
int[] x =
new int[10]; |
| Arrays (dynamic) |
#include <stdlib.h> int* x = (int *) malloc(10*sizeof(int)); |
int* x =
new int[10]; |
int[] x =
new int[10]; |
| Arrays (references) |
x[i] // subscript *(x + i) // pointer |
x[i] // subscript *(x + i) // pointer |
x[i] // subscript only |
| Output | #include <stdio.h>
printf("%i\n", x[i]); |
#include <iostream> using std::cout; cout << x[i] << "/n"; |
System.out.print(
x[i] + "\n"); |
| Boolean | 1 or any int != 0 is true 0 is false |
bool a = true; bool b = false; |
boolean a = true; boolean b = false; |
| while loop do while loop |
int i = 10; while(i--) x[i] = 0; |
int i = 10; while(i--) x[i] = 0; |
int i = 10; while(i-- != 0) x[i] = 0; |
| for loop | int i; for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) x[i] = 0; |
for (int i = 0;
i < 10; i++)
x[i] = 0; |
for (int i = 0;
i < 10; i++)
x[i] = 0; |
| main function |
int main(void) { }
int main(int argc,
char* argv[]) { } |
int main() { }
int main(int argc,
char* argv[]) { } |
public static void
main(String[] args) {
} |
| function prototypes |
If no prototype or definition, function returns int |
Prototype or definition required before use |
Only in an interface. No def required before use. |